mmdet 3: Customize Data Pipelines
TUTORIAL 3: CUSTOMIZE DATA PIPELINES
Design of Data pipelines
Following typical conventions, we use Dataset and DataLoader for data loading with multiple workers. Dataset returns a dict of data items corresponding the arguments of models’ forward method. Since the data in object detection may not be the same size (image size, gt bbox size, etc.), we introduce a new DataContainer type in MMCV to help collect and distribute data of different size. See here for more details.
The data preparation pipeline and the dataset is decomposed. Usually a dataset defines how to process the annotations and a data pipeline defines all the steps to prepare a data dict. A pipeline consists of a sequence of operations. Each operation takes a dict as input and also output a dict for the next transform.
We present a classical pipeline in the following figure. The blue blocks are pipeline operations. With the pipeline going on, each operator can add new keys (marked as green) to the result dict or update the existing keys (marked as orange). 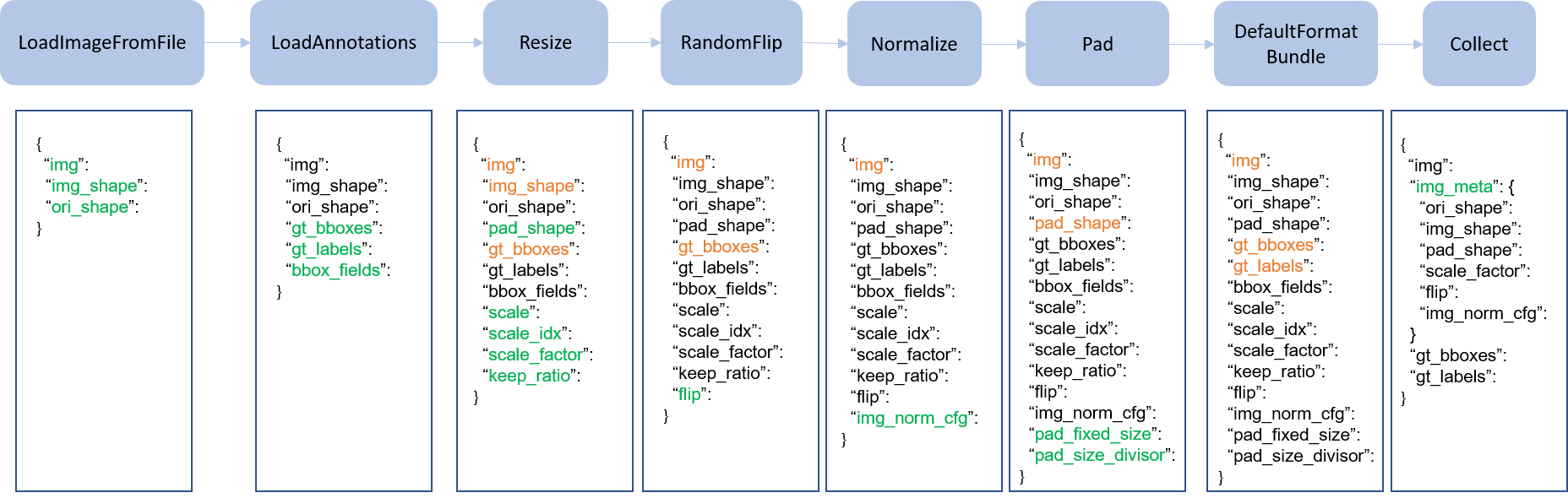
The operations are categorized into data loading, pre-processing, formatting and test-time augmentation.
Here is a pipeline example for Faster R-CNN.
img_norm_cfg = dict(
mean=[123.675, 116.28, 103.53], std=[58.395, 57.12, 57.375], to_rgb=True)
train_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(type='LoadAnnotations', with_bbox=True),
dict(type='Resize', img_scale=(1333, 800), keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='RandomFlip', flip_ratio=0.5),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='Pad', size_divisor=32),
dict(type='DefaultFormatBundle'),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img', 'gt_bboxes', 'gt_labels']),
]
test_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(
type='MultiScaleFlipAug',
img_scale=(1333, 800),
flip=False,
transforms=[
dict(type='Resize', keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='RandomFlip'),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='Pad', size_divisor=32),
dict(type='ImageToTensor', keys=['img']),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img']),
])
]
For each operation, we list the related dict fields that are added/updated/removed.
Data loading
LoadImageFromFile
- add: img, img_shape, ori_shape
LoadAnnotations
- add: gt_bboxes, gt_bboxes_ignore, gt_labels, gt_masks, gt_semantic_seg, bbox_fields, mask_fields
LoadProposals
- add: proposals
Pre-processing
Resize
- add: scale, scale_idx, pad_shape, scale_factor, keep_ratio
- update: img, img_shape, *bbox_fields, *mask_fields, *seg_fields
RandomFlip
- add: flip
- update: img, *bbox_fields, *mask_fields, *seg_fields
Pad
- add: pad_fixed_size, pad_size_divisor
- update: img, pad_shape, *mask_fields, *seg_fields
RandomCrop
- update: img, pad_shape, gt_bboxes, gt_labels, gt_masks, *bbox_fields
Normalize
- add: img_norm_cfg
- update: img
SegRescale
- update: gt_semantic_seg
PhotoMetricDistortion
- update: img
Expand
- update: img, gt_bboxes
MinIoURandomCrop
- update: img, gt_bboxes, gt_labels
Corrupt
- update: img
Formatting
ToTensor
- update: specified by
keys.
ImageToTensor
- update: specified by
keys.
Transpose
- update: specified by
keys.
ToDataContainer
- update: specified by
fields.
DefaultFormatBundle
- update: img, proposals, gt_bboxes, gt_bboxes_ignore, gt_labels, gt_masks, gt_semantic_seg
Collect
- add: img_meta (the keys of img_meta is specified by
meta_keys) - remove: all other keys except for those specified by
keys
Test time augmentation
MultiScaleFlipAug
Extend and use custom pipelines
- Write a new pipeline in a file, e.g., in
my_pipeline.py. It takes a dict as input and returns a dict.import random from mmdet.datasets import PIPELINES @PIPELINES.register_module() class MyTransform: “””Add your transform Args: p (float): Probability of shifts. Default 0.5. “”” def __init__(self, p=0.5): self.p = p def __call__(self, results): if random.random() > self.p: results[‘dummy’] = True return results - Import and use the pipeline in your config file. Make sure the import is relative to where your train script is located.custom_imports = dict(imports=[‘path.to.my_pipeline’], allow_failed_imports=False) img_norm_cfg = dict( mean=[123.675, 116.28, 103.53], std=[58.395, 57.12, 57.375], to_rgb=True) train_pipeline = [ dict(type=‘LoadImageFromFile’), dict(type=‘LoadAnnotations’, with_bbox=True), dict(type=‘Resize’, img_scale=(1333, 800), keep_ratio=True), dict(type=‘RandomFlip’, flip_ratio=0.5), dict(type=‘Normalize’, **img_norm_cfg), dict(type=‘Pad’, size_divisor=32), dict(type=‘MyTransform’, p=0.2), dict(type=‘DefaultFormatBundle’), dict(type=‘Collect’, keys=[‘img’, ‘gt_bboxes’, ‘gt_labels’]), ]
- Visualize the output of your augmentation pipelineTo visualize the output of your augmentation pipeline,
tools/misc/browse_dataset.pycan help the user to browse a detection dataset (both images and bounding box annotations) visually, or save the image to a designated directory. More detials can refer to useful_tools